The gender identification of transgender individuals differs significantly from individuals assigned or birth sex. It is common for emotions of pain and distress to result from this incongruence. A process of gender transition, which may involve several treatments and surgeries to match one’s physical appearance with one’s gender identification, is something that many transgender individuals choose to go through. Feminization practices are an important part of the gender transition for transgender women who were born with a male gender identity. These surgical and non-surgical procedures are intended to give the body a more feminine appearance, and they are frequently pursued in conjunction with hormone therapy and counseling.
We will discuss both surgery and non-surgical feminization techniques for transgender individuals in this post. It is significant to keep in mind that these procedures are very customized. To protect individuals’ well-being during the transition process, transgender patients will frequently have rigorous psychiatric evaluations and follow-up care before and after these surgeries.
Hormonal Treatments in Transgender Feminization
Understanding the function of hormonal therapy in the process is crucial before diving into the intricacies of surgical and non-surgical feminization methods. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is frequently used by transgender women to encourage the development of secondary sexual traits consistent with individual gender identity. The usage of estrogen and anti-androgen drugs is required for this.
Estrogen Therapy: The main hormone that contributes to the body’s development of feminine features is estrogen. Transgender women can consume estrogen orally, intravenously, or topically.
Breast development, softer skin, and fat redistribution to the hips and thighs are possible side effects of estrogen therapy.
Anti-Androgen Therapy: Anti-androgens are drugs that block the effects of testosterone and other male sex hormones. Anti-androgens serve to prevent or stop the development of male characteristics including facial hair and muscle mass by lowering the influence of testosterone. Although hormone therapy is a crucial component of feminization, many transgender women find that it is insufficient to produce the necessary physical changes on its own. The goal of both surgery and non-surgical therapies is to progressively feminize the body.
Surgical Feminization Procedures
Transgender women who seek a more comprehensive feminization of their bodies often consider surgical procedures. These surgeries are typically performed by specialized surgeons who have experience in transgender healthcare. The specific procedures may vary based on individual needs, goals, and available options. Common surgical feminization procedures include:
Facial Feminization Surgery (FFS):
FFS encompasses various procedures such as forehead contouring, rhinoplasty (nose surgery), chin reduction, and Adam’s apple reduction (tracheal shave).
FFS aims to soften masculine facial features and create a more feminine appearance.
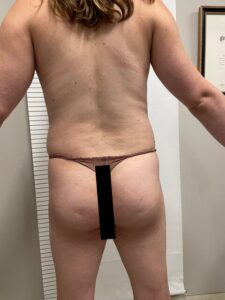
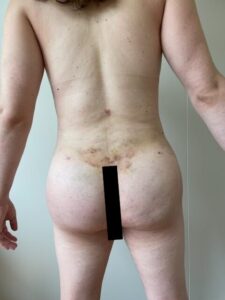
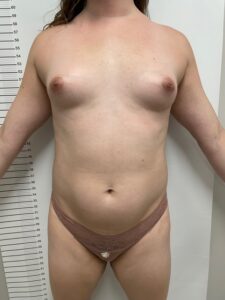
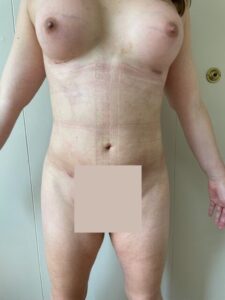
Breast Augmentation:
Many transgender women opt for breast augmentation to achieve a more feminine chest profile.
This procedure involves the placement of breast implants or, in some cases, fat grafting to enhance breast size and shape.
Our office doesn’t offer vaginoplasty, nor orchiectomy, or voice feminization/hair removal
Vaginoplasty:
Vaginoplasty is a gender-affirming surgery that involves the construction of a neo-vagina. This procedure may include penile inversion or other surgical techniques to create a functional and aesthetically pleasing vaginal structure.
Orchiectomy:
An orchiectomy is the removal of the testicles, which reduces the production of testosterone. It is a common surgical step for transgender women undergoing gender confirmation procedures.
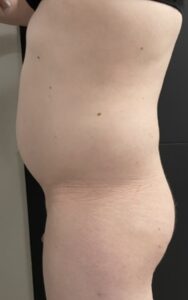
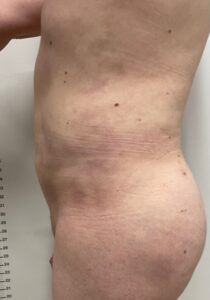
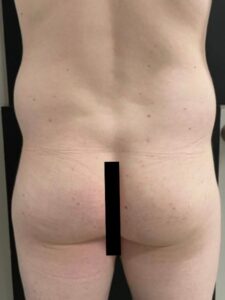
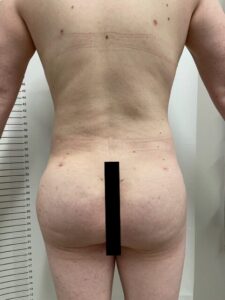
Liposuction and Fat Grafting:
Vaginoplasty:
Vaginoplasty is a gender-affirming surgery that involves the construction of a neo-vagina. This procedure may include penile inversion or other surgical techniques to create a functional and aesthetically pleasing vaginal structure.
Orchiectomy:
An orchiectomy is the removal of the testicles, which reduces the production of testosterone. It is a common surgical step for transgender women undergoing gender confirmation procedures.
Liposuction and Fat Grafting:
Liposuction can be used to shape the body by removing excess fat from specific areas, while fat grafting can enhance curves in areas like the buttocks and hips.
Voice Feminization Surgery:
Some transgender women opt for voice feminization procedures to modify individuals pitch and speech patterns to sound more feminine.
Hair Removal:
Many transgender women undergo permanent hair removal procedures, such as electrolysis or laser hair removal, to eliminate facial and body hair. It is important to emphasize that the choice of surgical procedures is highly individual, and not all transgender women pursue all of these options. The decision to undergo surgery depends on factors like individual goals, financial considerations, and medical eligibility.
Non-Surgical Feminization Procedures
Non-surgical procedures play a crucial role in feminization and are often used in conjunction with surgical interventions. These non-invasive options can be a more affordable and accessible way to achieve a more feminine appearance. Common non-surgical feminization procedures include:
Makeup and Cosmetics: Skilled makeup application can significantly alter facial features, providing the illusion of a more feminine appearance.
Wig and Hair Styling: Wigs and hairstyling can help transgender women create the hairstyle and hair length that best suits individuals gender identity.
Voice Training: Voice training with a speech therapist can help transgender women develop a more feminine voice.
Clothing and Fashion: Choosing clothing that complements body shape and enhances femininity is a non-surgical method for achieving a more feminine appearance.
Body Shaping Garments: Shapewear and undergarments can help create curves and enhance the silhouette, making clothing fit more femininely.
Psychological Assessment and Support
Transgender individuals seeking feminization procedures are typically required to undergo psychological assessments to ensure they are making informed and emotionally stable decisions. These assessments assess mental health, readiness for the transition process, and the ability to cope with potential stressors. Moreover, psychological support is crucial throughout the entire transition process to help individuals navigate the emotional challenges that can arise.
Wrapping Up
Transgender feminization procedures are a vital component of the gender transition process for transgender women. These procedures, which encompass both surgical and non-surgical options, aim to align the individual’s physical appearance with their gender identity. While these procedures are significant, they are only one aspect of a multifaceted journey that often includes hormone therapy and psychological support. It is essential to approach each transgender individual’s unique needs and goals with sensitivity and respect, recognizing that the path to self-discovery and self-acceptance.
As societal understanding of gender diversity continues to evolve, transgender individuals must have access to appropriate healthcare, support, and resources to facilitate individuals’ gender-affirming journey. Advocacy for transgender rights, healthcare access, and destigmatization is essential in fostering a more inclusive and compassionate society for all individuals, regardless of individual gender identity.